Terminologies and buzzwords can be very confusing. They can even negatively impact your buying decision. This is specifically true in the world of hosting and servers. If you just go by the marketing terms without knowing what they truly imply, you are in for a rude shock. So, in the article, we’ll go back to the basics and learn what exactly web hosting and cloud hosting mean. Are these two terms used correctly? Let’s find out.
Understanding Web Hosting
Across the internet, you will find many different definitions of web hosting. But generally, we use the term ‘web hosting’ to mean those services that are used to host websites. The primary purpose of a web hosting service is to host websites. It can be used for other purposes, but people generally don’t use a web hosting service for those purposes.
Features of web hosting:
The features of web hosting revolve around hosting websites. These are the main features of any web hosting service:
A server that’s optimized for storing and processing HTML, CSS and JavaScript files
The servers provided by web hosting companies are optimized to store and process HTML, CSS and Javascript files - the building blocks of any website. It’s possible that an advanced web hosting server can be used for other purposes like crunching big data and hosting complex applications. However, the primary purpose of traditional web hosting is to store and process HTML, CSS and JS files.
Shared hosting, VPS, and Dedicated Hosting - all three major kinds of hosting are provided
A typical web hosting service will invariably offer a shared hosting plan - where the computing resources - RAM, processor power, bandwidth etc are shared with other accounts. This means you are not the only tenant of the resources. A web hosting service also offers VPS hosting where the underlying hardware is logically (by means of virtualization) isolated so that you get a fixed amount of computing resources that you won’t be sharing with others. This logical isolation also makes VPS more secure than shared hosting.
Providers of more advanced web hosting services provide dedicated web hosting where you rent the entire underlying hardware. This means you get root access to the underlying OS and can customize the server as you see fit.
Usage of a fixed amount of computing resources
Most traditional web hosting services offer a fixed amount of computing resources. This means you will NOT be using a pay-as-you-go model. You buy a specific amount of computing resources and storage for a specific sum of money.
Pros and Cons of a Traditional Web Hosting Service
Traditional web hosting services come with both benefits and disadvantages. Here’s a list of major pros and cons that come with traditional web hosts:
Pros:
- Web hosting services are typically less complex. The technical backend (excluding that of a dedicated web host) is more or less managed by the service provider. This makes it incredibly easy for a person to host websites and applications without worrying too much about the technicalities.
- Since the technological backend is managed by the web hosting provider itself, the responsibility of keeping the instance secure falls mostly on the provider. This is a pro in terms of managing the instance. But this can be a problem as well. We will talk about it in the following section.
- When you opt for a traditional web hosting service, you prepay for a specific amount of computing resources - there is no chance for you to overuse the resources. Hence, you won’t face any rude cost-shock.
Cons
- Since web hosting services aren’t that complex, you can’t customise them as you wish. This can be a problem if your application requires a specific configuration.
- Most so-called affordable web hosting services employ poor backup best practices. Even if they back up your data, usually, they keep the backup in the same data centre. This can be a huge issue in case a physical incident (fire, flood etc.) happens in the place where the data centre is located.
- Since the security of the servers is managed by the web hosting company, if there is any lapse in their security posture, you can’t do anything about it.
- But the biggest problem with web hosting is the fact that you can’t scale up or down the computing resources on an on-demand basis. When you scale up, you need to buy additional resources for a specific period, and you have to expect downtime while they move your IT workload to the upgraded server.
Understanding Cloud Hosting
“Cloud” Is a Marketing Term: Don’t Get Confused
Today, more and more companies are using the term - ‘Cloud’ to earn marketing brownie points. Anything computing service that is accessed using the web is termed a cloud. This can be very confusing for businesses that are actively searching for cloud services. So, what exactly is cloud hosting? And how is it different from traditional hosting? Let’s find out.
What Is Cloud Hosting From a Technical Point of View?
From a technical point of view, cloud hosting services use a cluster of servers to build a single platform and use virtualisation technology to allocate resources to customers.
To make it more clear, cloud platforms like AWS or Azure have huge data centres and a huge amount of hardware like physical CPU cores, SSDs, RAM etc. Now, these cloud platforms use hypervisor and virtualisation technologies to convert these PHYSICAL resources to LOGICAL resources. The benefit? It can flexibly scale up and down the resources for customers upon request.
A typical cloud hosting is made up of the following:
- Physical hardware like processor, processor cores, RAM, SSDs etc.
- Virtualized CPU or vCPU. In the case of AWS, one vCPU represents one thread of a physical core.
- Hypervisor
- Virtualized memory allocation
- Virtualized SSD or NvME storage
- Virtualized network configuration
- Virtualized OS
- Load balancers
- Other cloud-specific technologies
What Is Cloud Hosting From a Marketing Point of View?
From the marketing point of view, any hosting services that can be accessed via the web can be termed as ‘cloud hosting.’ This is where the confusion starts. Companies can term their dedicated hosting services as cloud hosting services. The problem with this approach is that - by this definition, there isn’t much difference between AWS/Azure and traditional dedicated web hosting. However, in reality, there is a huge difference between the two forms of hosting.
So, true cloud hosting refers to those hosting services where a cluster of servers is used to build a unified platform.
Pros and Cons of Cloud Hosting
Although cloud hosting is regarded as the marvel of modern hosting, it has both pros and cons.
Pros of Cloud Hosting
- Scalability is the biggest advantage of cloud hosting. Unlike traditional web hosting, where you buy a specific amount of computing resources for a specific period, in the case of cloud hosting, you can opt for the pay-as-you-go model. You can start with low storage and low computing resources and scale up the resources as and when needed.
- The pay-as-you-go model reduces the upfront cost associated with buying or renting computing resources from traditional web hosts.
- Cloud hosting is optimized for all kinds of purposes - not just for hosting websites. From hosting applications to crunching big data, from real-time data analytics to IoT and Machine Learning - cloud hosting is optimized for anything and everything. This makes it more powerful than traditional hosting.
- Cloud hosting offers more control over the environment and instances. You can configure the network and the available resources to suit your needs. And when it comes to dedicated cloud hosting services, you get to configure the setup on a hardware level.
- Cloud hosting providers take backing up the IT resources and enterprise data of clients extremely seriously. You can make backups of your data in different availability zones. As a result, even if something physically happens to the data centre in one region, the replication of the instances and the data in another server will be ready to take over.
Cons of Cloud Hosting
- Cloud hosting abstracts away the infrastructure used by companies. While this abstraction makes everything smooth and seamless, it can bring additional complexities. Since the underlying hardware details remain hidden, the lack of visibility can sometimes prove to be a hindrance.
- Security of the IOT workload on the cloud platform is a shared responsibility. It’s not just the cloud provider that needs to be vigilant about the security of your instances and data, but you need to be vigilant as well. When it comes to network configuration and keeping the virtual OS secure and updated, the onus is on you.
- Hosting on the cloud might prove to be a DIY experience with little support from the cloud provider. While some cloud providers do provide managed services, you will still not get the same hand-holding as you get from traditional web hosts.
- Most cloud providers have their own ecosystem. Once you opt for a specific cloud provider, your application has to be configured, keeping its unique ecosystem in mind. The problem with this is the fact that your application gets locked into that specific ecosystem every passing day. You can avoid this by using multi-cloud, but it will bring additional costs and complexities into the picture.
You May Also Like: Top Factors to Consider When Choosing Your Cloud Hosting Provider
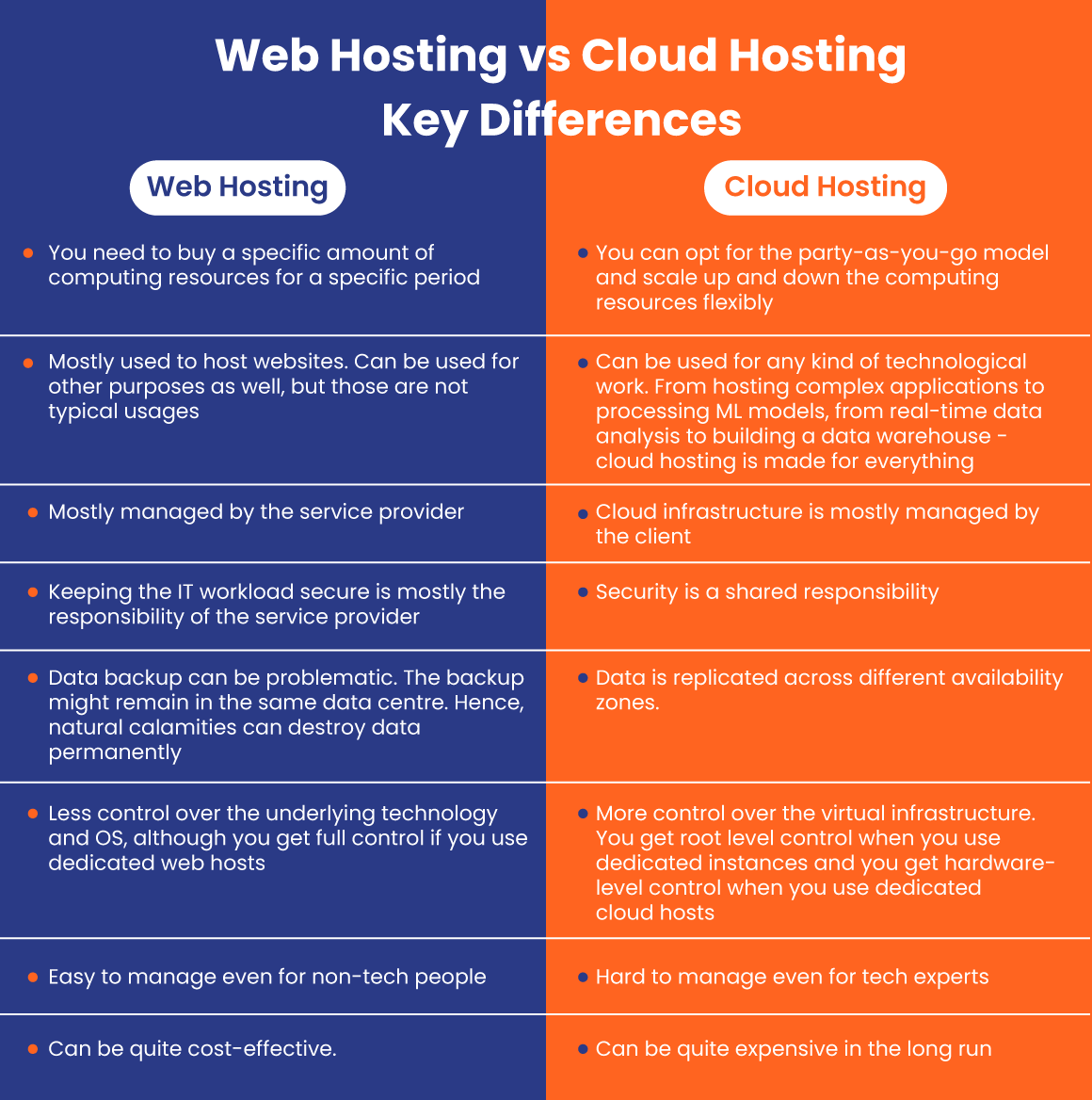
Web Hosting vs. Cloud Hosting: Key Differences
Choosing the Right Hosting Solution for Your Business
Now that you have a thorough idea about web hosting services and cloud hosting, it will become easier for you to choose the right solution.
If you have a business that’s not a multinational, if your business does not have more than 1000 employees, if your application isn’t that complex, then maybe cloud computing will be an overkill for you.
On the other hand, if your business works with big data, real-time data analytics, Machine Learning, IoT etc, then cloud computing can keep your business agile. With cloud computing, you don’t need to buy advanced hardware - you can use the cloud infrastructure on a pay-as-you-basis.
Today traditional cloud hosting services can offer the same level of services that are provided by AWS or Azure. For example, Silver Touch Technologies - one of the best cloud hosting providers in India - provides Linux servers with 4 vCPU and 16GB RAM at just Rs. 7,199 per month. At the same time, you get phenomenal customer support.
Conclusion
The decision to use either traditional web hosts or cloud hosts depends largely on the budget, the size of the company and its purpose. For most use cases, traditional cloud hosts can be used to host business-critical applications. For cutting-edge solutions, cloud hosting is more suitable. However, more and more businesses prefer a hybrid setup where they use AWS or Azure for some purposes, and for other purposes, they use either on-prem servers or traditional web hosting. The future is hybrid.
FAQs
What is web hosting?
Web hosting is a service that provides the infrastructure and resources needed to store and serve websites on the internet.
What is cloud hosting?
Cloud hosting is a type of hosting that uses virtualization technology to allocate and manage computing resources across a network of servers.
What are the main features of web hosting?
Web hosting primarily focuses on hosting websites and offers shared hosting, VPS hosting, and dedicated hosting plans.
What are the key advantages of cloud hosting?
Cloud hosting offers scalability, flexibility, and optimization for various purposes, including hosting applications, big data processing, and more.
How do I choose between web hosting and cloud hosting for my business?
Your choice depends on factors like your budget, company size, and the complexity of your applications. Web hosting suits simpler needs, while cloud hosting is ideal for scalability and diverse applications.